Asset Publisher
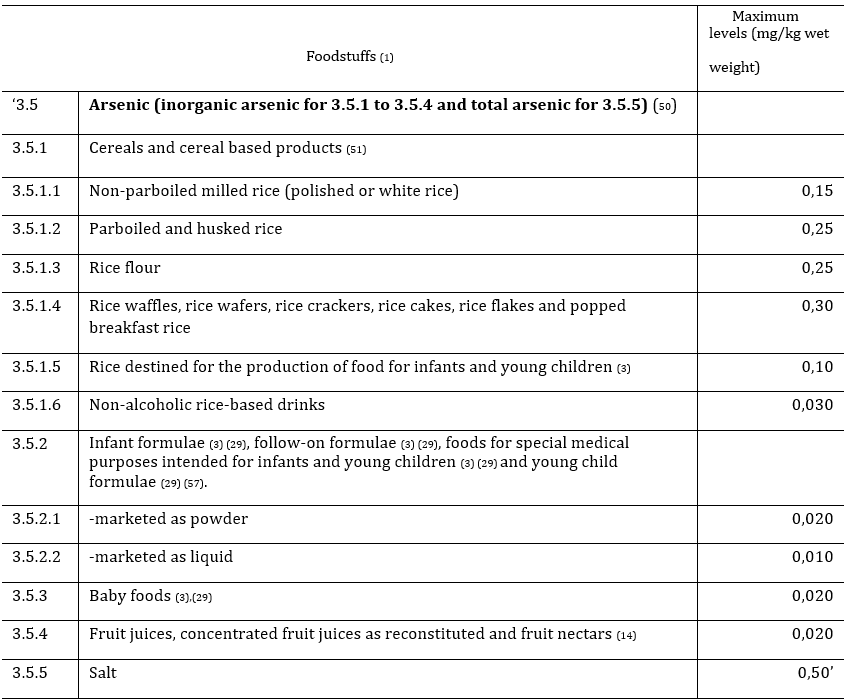
The European Commission has amended Commission Regulation (EC) No. 1881/2006 with respect to the maximum levels of arsenic (inorganic) in certain foods, which will be effective by 26th March 2023.
Arsenic is a metalloid commonly found in low concentrations in rocks, soil, and natural groundwater. However, human activities such as industrial emissions and the use of arsenic in various products like fertilizers, wood preservatives, and pesticides have increased its presence in the environment. Exposure to arsenic can occur through the skin or inhalation, but the main sources of exposure are food and drinking water.
According to the FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives, exposure to inorganic arsenic has been linked to cancer of the lung, urinary bladder, and skin. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) reported in 2021 that rice, rice-based products, grains, grain-based products not containing rice, and drinking water were the main contributors to dietary exposure to inorganic arsenic across different age groups. Additionally, certain foods like infant formula, baby foods, fruit juices, and cereal-based foods for young children can also contribute in dietary exposure to inorganic arsenic.
The table below lists the products and their respective maximum levels of inorganic arsenic under the Annex of the Commission Regulation (EU) 2023/465: